The term beamforming refers to a method of directing a wireless signal towards a specific receiving device, whereas the alternative would be allowing the signal to spread in all directions from a transmitter the way it naturally would.
By focusing a signal in a specific direction, beamforming delivers higher signal quality to a receiver. This means information is transmitted faster and more accurately. Furthermore, this accuracy can be reached without boosting broadcast power.
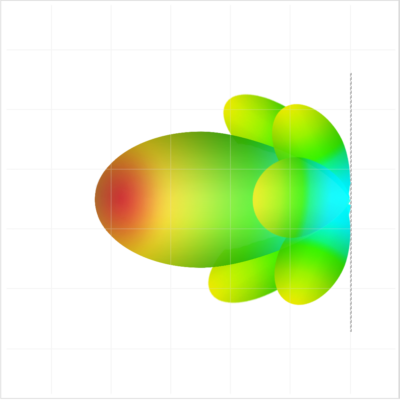
Example of Radiation Pattern with a Fixed Beamformer
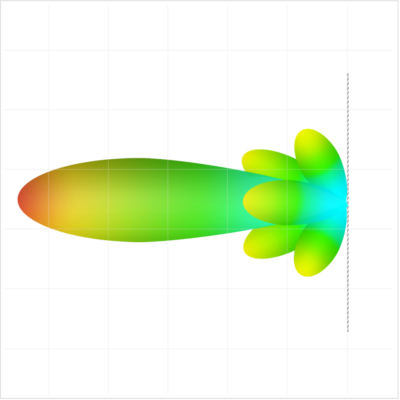
Example of Radiation Pattern with an Adaptive Beamformer
An antenna array is comprised of multiple radiating elements, each of which contributes an element pattern to the array’s radiation pattern. Each element pattern is a spatial distribution of RF power arising from the amplitude and phase of the RF signal at the element’s RF feed point. The array’s radiation pattern is determined by the coherent sum of all element fields, each which may be “weighted” by an additional amplitude and phase. Such weighted patterns exemplify beamforming in the array, whereby sidelobe levels and nulls are produced and controlled by adjusting the element weights.
Beamforming techniques loosely fall into two categories: conventional and adaptive.
Fixed beamforming generally describes a conventional technique where the antenna array pattern is obtained from fixed element weights that do not depend on the signal environment. Conversely, adaptive beamforming element weights that do depend on —and can adapt to— the signal environment via some feedback mechanism.
Adaptive beamforming, which was initially developed in the 1960s, uses a digital signal processor (DSP) to compute the complex weights using an adaptive algorithm, which then generates an array factor for an optimal signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR). Basically, adaptive beamformers are designed to adjust to differing situations in order to maximize or minimize SINR, which helps measure the quality of wireless communication.
The average civilian experiences adaptive beamforming technology in their every day life. In fact, wireless carriers use this technique to provide next-generation wireless communications (5G) and long-term evolution (LTE) services.
Latest Posts

7 Reasons for Enhancing RF Security in a Connected World
In this post, we discuss 7 reasons why bolstering RF security is a crucial element of national security, public safety, and economic stability.
A Closer Look at Horn Antennas
In a previous post, we introduced the history behind the horn antenna. In this post, we talk more about the horn antenna’s design, as well as what makes it so versatile. Horn antennas are named for their horn-like shape and come in a variety of designs.

5 Ways Physical Objects Affect RF Transmissions
In this post, we elaborate further on how physical objects can affect radiofrequency signal transmissions.
