Which Antennas are Suitable for Sensor Systems?
January 2025Sensor antennas are specialized antennas designed to transmit or receive electromagnetic signals in systems that detect, measure, or monitor physical, environmental, or biological parameters. These antennas serve as the communication interface between the sensor and the external system, enabling wireless data transmission, signal reception, or both.
Many sensor antenna designs are relatively compact in size, allowing them to be portable. Also, they’re often optimized for power-constrained environments, ensuring effective communication with minimal energy consumption.
Sensor antennas play a crucial role in various applications, including environmental monitoring, wireless sensor networks (WSNs), IoT devices, and industrial automation, medical devices, radar and navigation. These antennas come in different types, each designed for specific sensor systems and frequency ranges.
Here are some common types of sensor antennas:
Dipole antennas are a popular choice for sensor systems due to their simple design, reliable performance, and compatibility with a wide range of applications. One of their many benefits is that they can be scaled or adapted to specific frequencies by adjusting their length.
JEM Engineering’s UVW-0430B, the UHF Dipole Blade Antenna, is suitable for sensor systems, among other applications.
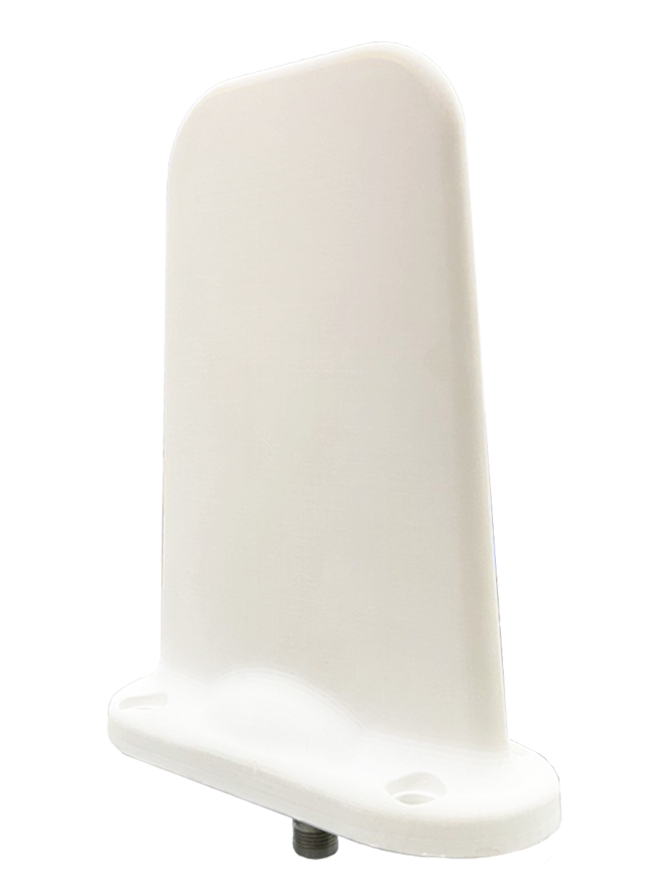

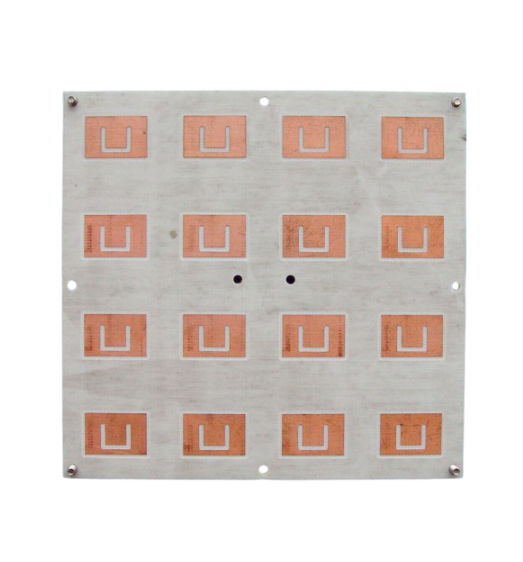
Lightweight and compact, patch antennas, also known as microstrip antennas, are also suitable for high-frequency applications and sensor applications, particularly in GPS sensors, RFID systems, and wearable devices. These are flat, low-profile antennas mounted on a substrate. Not only are they cost-effective, they are also easy to integrate, in that they can easily be be made to match the typical operational range of many sensors, such as those in smart homes or industrial IoT.
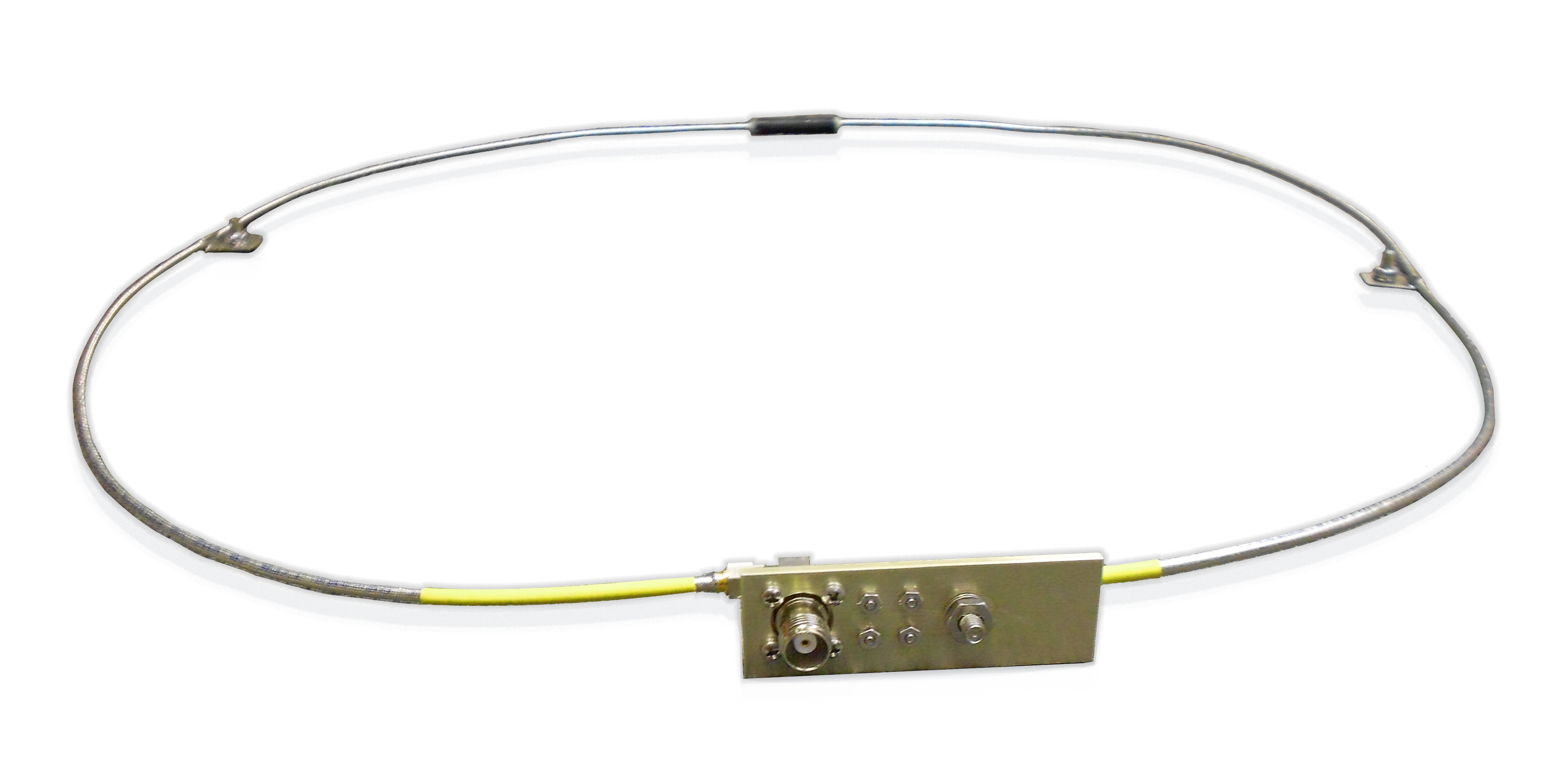
While patch antennas are suitable for high-frequency applications, loop antennas are better suited for low-frequency applications. Loop antennas can be formed in a circular, square, or rectangular loop shape. They can be used for RFID systems as well as magnetic field sensing.
JEM Engineering’s line of loop antennas includes flexible, as well as rigid designs.
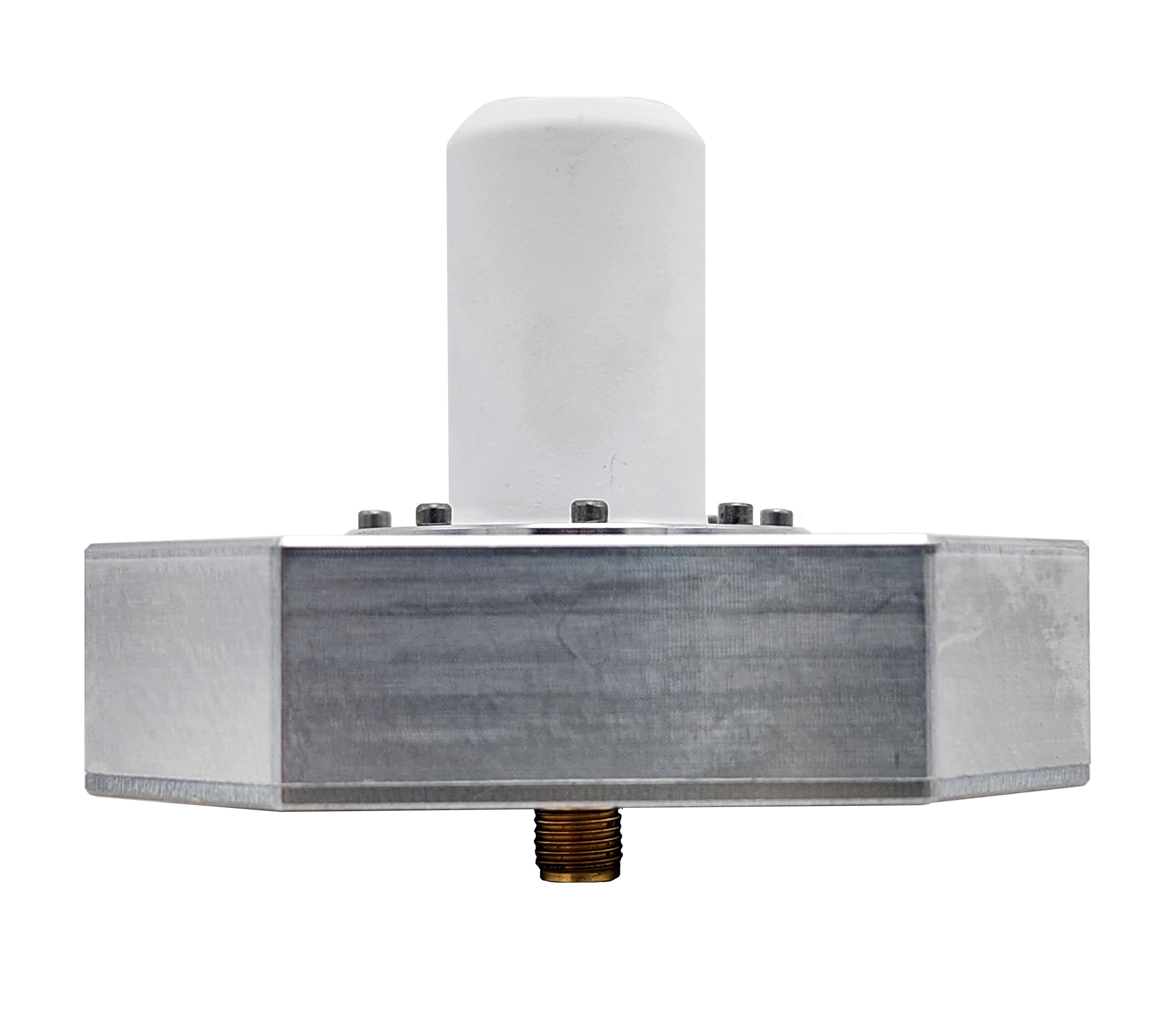


Helical, or “helix” antennas, made of wire wound in the shape of a helix. They are circularly polarized and boast good directional properties. These antennas are suitable for satellite communication sensors, IoT devices, and GNSS systems.
The QHA-678 or MUOS SATCOM Quadrifilar Helix Antenna is an example of an antenna suitable for SATCOM sensors.
Horn antennas, which are flared designs that direct signals into free space, feature high gain, directional radiation, and broad bandwidth. They are most suitable for radar sensors, automotive collision avoidance systems, as well as high-frequency sensing.
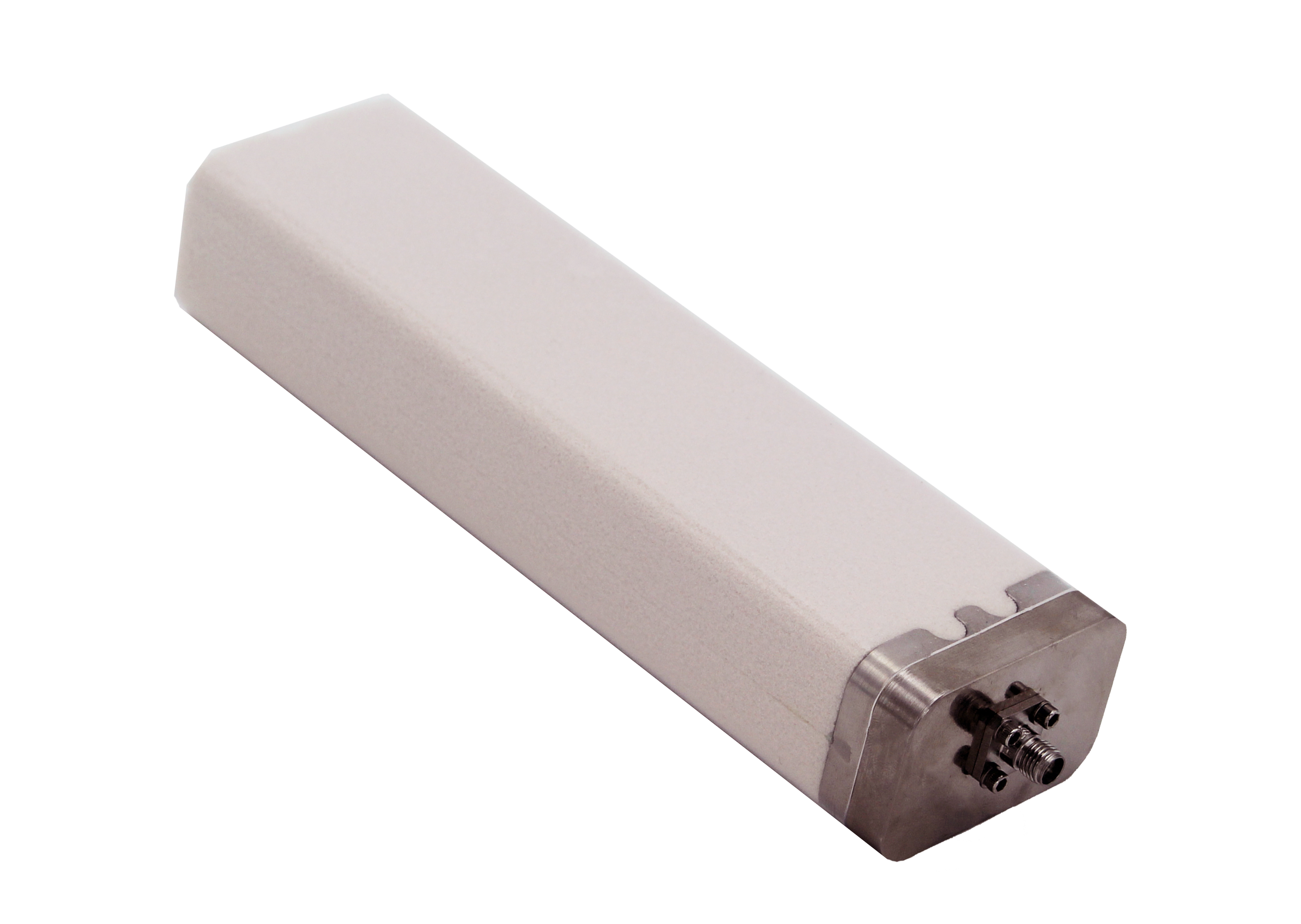


Slot antennas, which are antennas with a slot cut into a conductive surface, are also good designs for sensor systems.
Vivaldi antennas, which are slot antennas of a particular formation, are a good choice for sensor applications, particularly requiring wide bandwidth, high directionality, or operation in higher frequency ranges.
Active Electronically Steered Arrays (AESAs) are highly suitable for certain sensor systems, especially those requiring high performance, adaptability, and advanced features. AESAs excel in applications where precision, speed, and multi-functionality are critical. They deliver high precision and resolution, fast scanning and beam steering, and enhanced sensitivity. They also allow for customization for different applications. from small drones to large-scale ground-based radar systems.
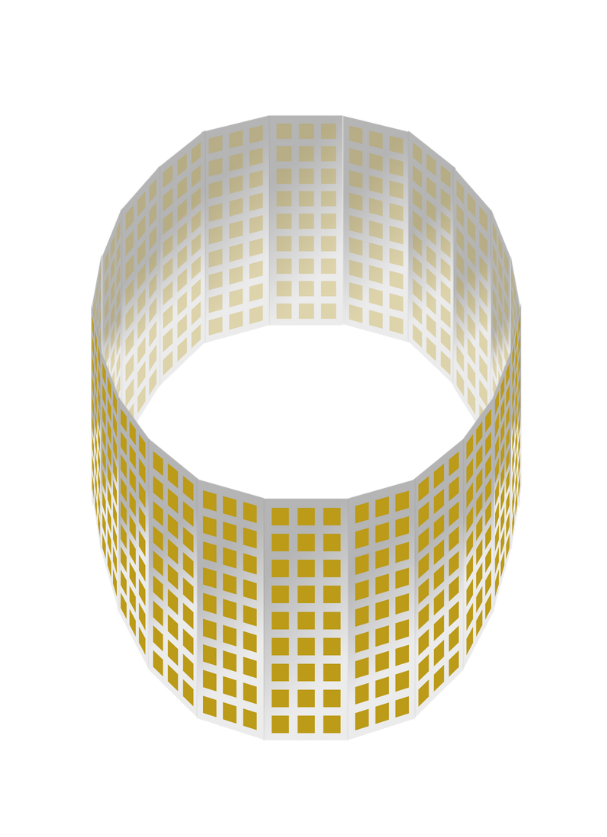
Active Electronically Steered Arrays (AESAs) are highly suitable for certain sensor systems, especially those requiring high performance, adaptability, and advanced features. AESAs excel in applications where precision, speed, and multi-functionality are critical. They deliver high precision and resolution, fast scanning and beam steering, and enhanced sensitivity. They also allow for customization for different applications. from small drones to large-scale ground-based radar systems.
Latest Posts
Loop Antennas: Design Overview
Loop antennas come in many forms, but their overarching distinction is that they are relatively simply constructed, yet very versatile.
Antenna Development & Environmental Testing
Antenna environmental testing is a crucial part of its qualification.
What is Beamforming?
The term beamforming refers to a method of directing a wireless signal towards a specific receiving device, whereas the alternative would be allowing the signal to spread in all directions from a transmitter the way it naturally would.

Antenna Miniaturization
As the phrase suggests, antenna miniaturization is the process of replicating an antenna’s functionality while reducing its physical size.
