Taking Measurements with Drones
November 2023In a previous issue, we introduced UAVs. In another issue, we discussed how they’re used in defense. In this issue, we introduce the idea of using drones for taking measurements.
UAVs, also nicknamed, “drones,” are exceptional at capturing a bird’s-eye view. This is one of the main reasons why they’re becoming more popular for various measurement purposes. Measurement drones are equipped with sensors and cameras that allow for precise and accurate measurements in numerous fields.
1. Aerial Surveys and Mapping. UAVs equipped with cameras or LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) sensors can capture high-resolution aerial imagery to create detailed maps, 3D models, and topographic surveys. These maps can be used in urban planning, agriculture, construction, and land surveying.

2. Precision Agriculture. In addition to agricultural mapping, drones can use sensors to measure crop health and growth. They can analyze plant health, soil conditions, and irrigation needs. This data helps farmers optimize their crop yields and resource usage.
3. Environmental Monitoring. Drones can also be used for environmental measurements, such as assessing forest cover, monitoring wildlife populations, and measuring changes in landscapes over time. They can track changes in ecosystems and environmental factors like deforestation, water quality, or erosion.
4. Infrastructure Inspection. UAVs can inspect infrastructure like bridges, pipelines, and power lines by capturing detailed images and data for analysis. This way, they can help detect structural issues or areas that need maintenance.
5. Disaster Management. In emergency situations such as natural disasters, drones can quickly assess the extent of damage, locate survivors, and provide real-time information to emergency responders.
6. Remote Sensing and Geology. Drones can also collect data for geological surveys, identifying mineral deposits or geological formations. They can also assist in exploring hard-to-reach or dangerous terrains.

7. Construction and Development. Drones also have the ability to monitor construction sites, track progress, and create accurate measurements for construction projects. They help with volumetric measurements and track changes over time.
8. Scientific Research. Researchers use UAVs for various scientific studies, from atmospheric research to studying wildlife behavior. They can be equipped with specialized instruments to gather specific data.
Drones offer significant advantages in efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and safety compared to traditional methods of measurement and data collection. Their ability to access difficult or dangerous terrain and collect data from different perspectives makes them invaluable in various industries and fields.
Latest Posts
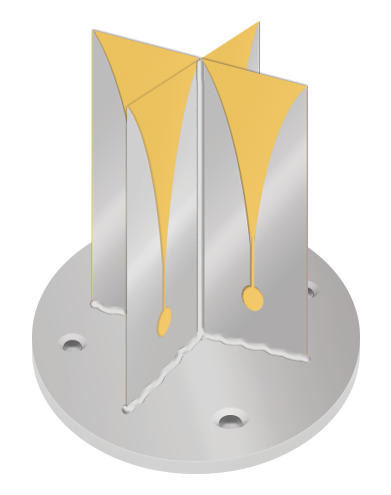
Anatomy of a Vivaldi Antenna
The Vivaldi antenna, also known as a tapered slot antenna, is a type of linear-polarized planar antenna invented by Peter Gibson in 1978…
Introduction to the Biconical Antenna
The phrase “biconical antenna” describes a broadband antennas that are made up of two roughly conical conductive objects, that are nearly touching at their points. Because of their configuration, they can also be referred to as “bowtie” or “butterfly” antennas.
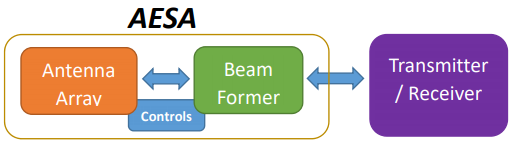
AESAs: Active Electronically Steered Arrays
AESA stands for Active Electronically Scanned Array or Active Electronically Steered Array.
