Antenna 101: Types and Applications
February 2018We are experts in custom antenna design and manufacturing for various applications. Some common applications include vehicular, airborne, communications, SIGINT (signal intelligence), and ISR (intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance). While certain antenna types are more suitable for each of these specific applications, many of our products are versatile and multi-platform.
In this article, we take a look at some of the different antenna types, and what applications they can be used for.
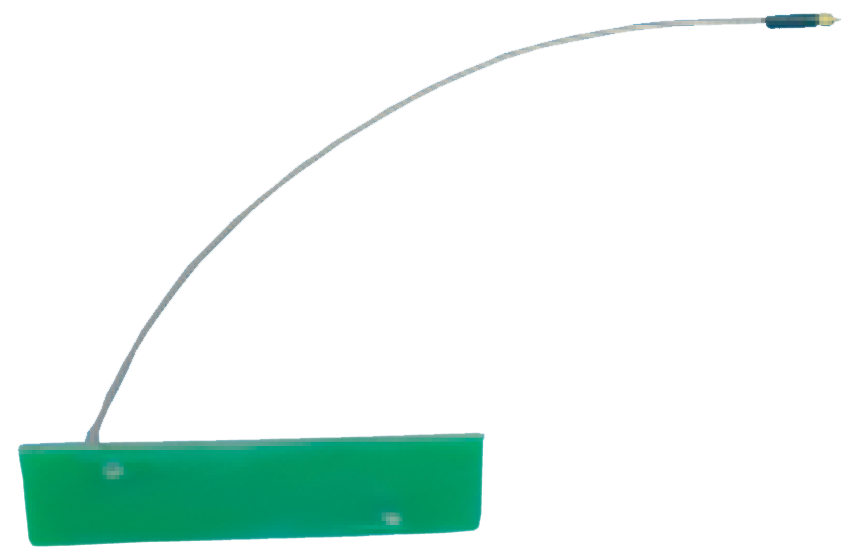
Broadband Antennas – These antennas operate over a wide band of frequencies, or “bandwidths.” Generally, the bandwidths over which they operate are higher than 1 octave. They come in a variety of forms, including spirals, log-periodic antennas, dipoles and Vivaldi notch elements
An example of a broadband antenna, the HSA-056 is a 6″ spiral ideally suited for handheld and vehicular applications. With its wide bandwidth, broad beamwidth, and high RF efficiency, the antenna is also suitable for applications such as SIGINT, EW, and wideband communications.
Narrowband Antenna – In contrast to broadband antennas, narrowband antennas operate over relatively narrow bandwidths, generally much less than 1 octave. Patch and resonant cavity antennas are typical examples of narrowband antennas.
The RDF-8696 is a narrowband transducer for short range reading and writing of RFID tags including GEN2 tags. Some of the applications it can be used for include printers and various forms of automation equipment.


Antenna Arrays & Beamformers – Array antennas consist of multiple radiating elements. In some cases, these elements are fed by a corporate power divider or “beamformer.” The simplest beamformer is a power division network, which yields a fixed radiation beam. A beamformer that incorporates controllable phase or delay elements is called a steerable beam array or “phased array.”
Also nicknamed the “Hexband Array,” the MBA-0127 is compact, low-profile, single-port antenna covering multiple bands from 400MHz to 2.2GHz. This array is useful for multiband communications, airborne applications, ISR applications, and SIGINT.
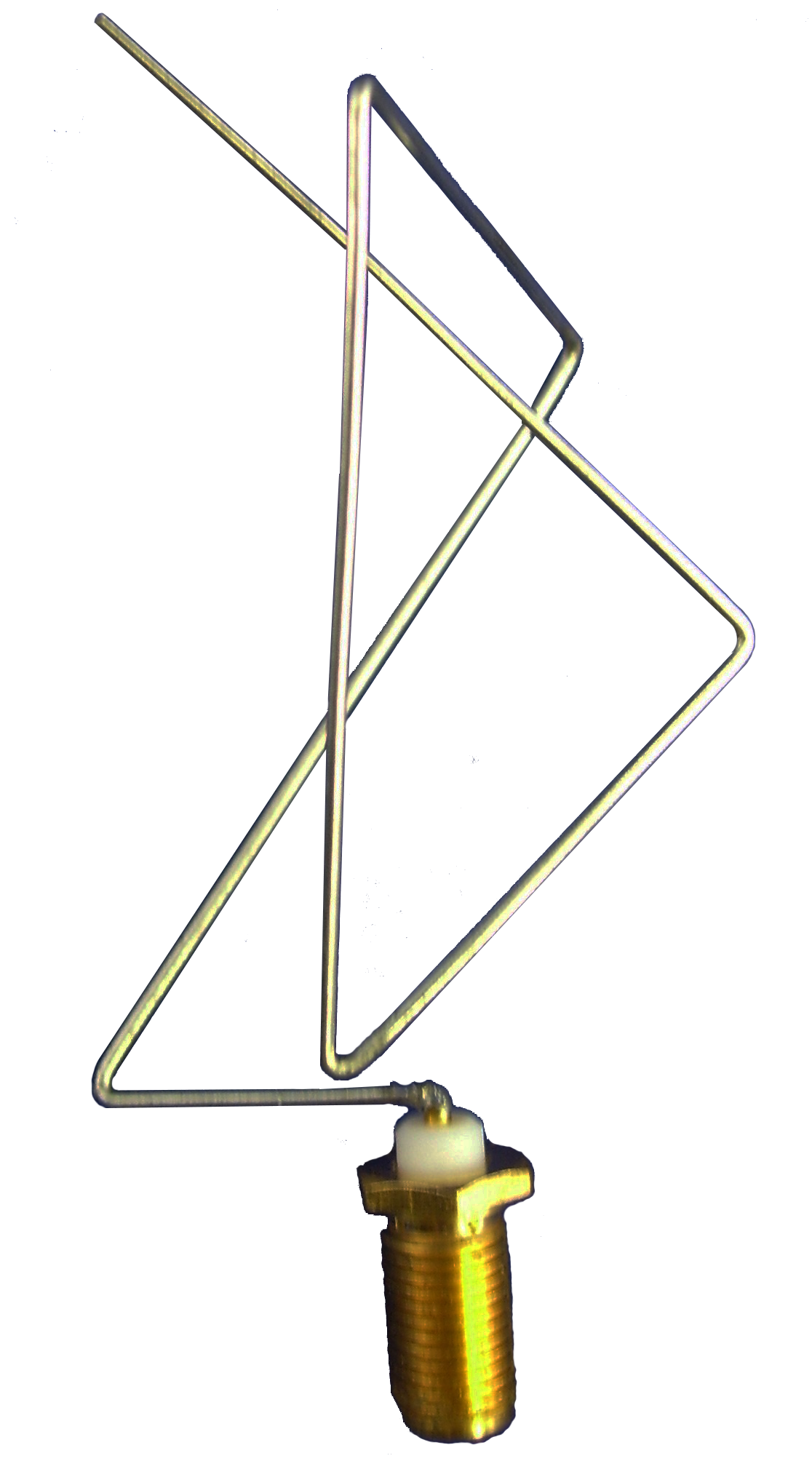
Genetic Antenna – These antennas are designed entirely by an optimization algorithm, which can be a genetic algorithm or some other iterative method. While many antennas are pre-existent designs that are modified through optimizations, these antennas are entirely new designs generated solely via computer.
Genetic antennas are perhaps the most unique, mainly because they are almost completely custom, like the one pictured here.
Latest Posts
The Outlook on Flat Panel Antennas
As the name suggests, a flat panel antenna, or FPA, is a simple directional antenna that is low-profile.

5G and Beyond
It’s very likely that you’ve heard the term “5G.” 5G means much more than faster speeds for one’s mobile devices. In this post, we briefly introduce 5G and contextualize the technology’s potential in the defense sector.

Scaling Unmanned Operations for Defense
In this post, we explore some of the opportunities and challenges facing unmanned operations in the defense sector.
Artificial intelligence (AI), which manifests itself in different forms, from website chat boxes to unmanned military operations, is broadly defined as any system or machine that is designed to imitate human intelligence, in order to perform tasks and improve upon itself using the increasing amount of information it collects.
